When a person is diagnosed with blocked heart arteries, the most common question that arises is whether they need angioplasty or bypass surgery. Both are proven and life-saving procedures, but they serve different purposes depending on the severity and location of blockages.
Understanding the difference between these two treatments can help patients and their families make informed decisions, reduce fear, and prepare better for treatment. This article explains both procedures in simple, patient-friendly language.
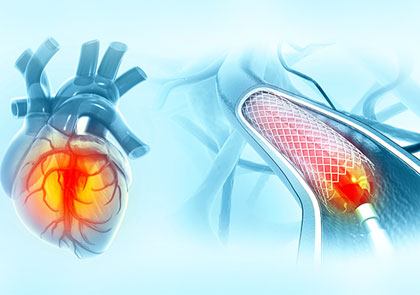
Angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure used to open blocked or narrowed heart arteries. A thin tube called a catheter is inserted through the wrist or groin and guided to the blocked artery. A small balloon is inflated to clear the blockage, and a stent (a tiny metal mesh tube) is placed to keep the artery open.
Angioplasty is commonly advised for patients with:
Bypass surgery, also known as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), is an open-heart surgical procedure. In this surgery, a healthy blood vessel is taken from the chest, leg, or arm and attached above and below the blocked artery to create a new pathway for blood to flow.
Bypass surgery is generally recommended for:
There is no single correct answer for all patients. The right treatment depends on several factors such as:
Some patients may be safely treated with angioplasty, while others may benefit more from bypass surgery for long-term survival.
Yes. In some cases, blockages can develop even after bypass surgery. Angioplasty may be performed later to treat these new blockages if required.
In many patients, early detection and timely angioplasty can prevent disease progression and delay or avoid the need for bypass surgery.
Both procedures are safe when performed in well-equipped cardiac centers. Angioplasty has lower immediate risk due to its minimally invasive nature, while bypass surgery offers better long-term protection in complex disease.
Both angioplasty and bypass surgery are proven, life-saving treatments for heart artery blockages. The choice depends on the patient’s heart condition, medical history, and overall health. The most important step is early diagnosis and timely treatment.
If you or your loved one is facing this decision, do not panic. A proper evaluation and clear guidance can help choose the safest and most effective treatment option for a healthy and active life ahead.